How it works
Summary
The R2Devops Dashboard uses various calculations with GitLab project CI/CD. The following sections will describe how it works.
CI/CD Engine
The Dashboard provides an overview of the CI/CD engines utilized within your entire GitLab organization.

Its purpose is to identify the CI/CD engines employed within your GitLab Organization and categorize into four different types:
- GitLab: When a project contains a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile at its root. - Jenkins: When a project contains a
JenkinsFileat the root, and/or awebhook, and/or aGitLab integration. - GitHub: When a project contains a
.github/workflowsdirectory. - No CI/CD: When a project doesn't match any of the previous cases, it's declared as having
No CI/CD.
It can assist in:
- Migrating old CI/CD engine implementations
- Preventing drift among the CI/CD engines used
- Identifying projects not utilizing CI/CD
A project could have multiple CI/CD engines. For example, project1 could have:
50%of GitLab50%of Jenkins
Pipeline Composition
The Dashboard provides an overview of your entire organization's CI/CD composition.
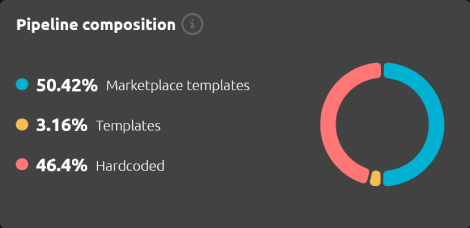
Its aim is to identify the types of templates utilized within your organization. For every GitLab project's CI/CD, we count all jobs and categorize them into:
- Hardcoded Job: A CI/CD job directly hardcoded inside the configuration file.
- Template: A CI/CD configuration template remotely included.
- Marketplace Template: A CI/CD configuration template remotely included, present within the R2Devops Marketplace.
This insight serves multiple purposes, such as:
- Identifying and reducing hardcoded jobs, which can accumulate technical debt.
- Transitioning to utilizing solely
Marketplace templates. - Follow adoption of
TemplatesorMarketplace templatesof your whole organization.
A project could be composed of a mix of multiple types. For example, project1 could have:
13.3%of Hardcoded Jobs24.3%of Templates62.4%of Marketplace Templates
Scores
The first dashboard tab is the overview page, offering a quick summary of projects within the current organization.
On this page, you'll find two global scores:
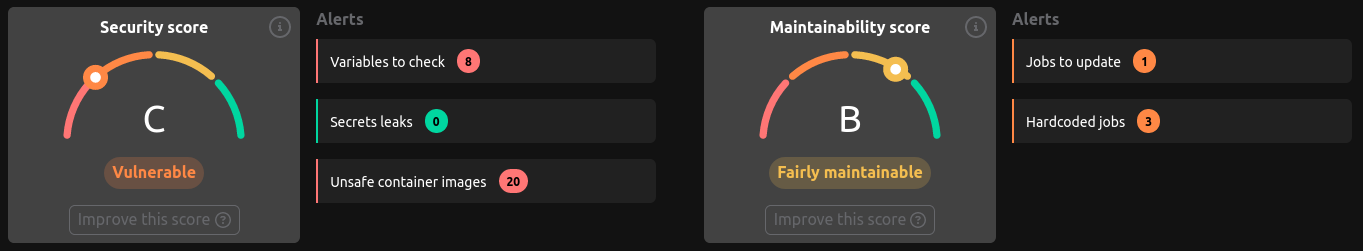
🛡️ Security Score
The security score is calculated based on the following criteria:
- Visibility and protection of CI/CD variables used in the configuration file (see Security/Variables tab)
- Detection of secrets leaks inside the CI/CD configuration file; we also scan the merged configuration (see Security/Secrets tab)
- Status of container images used in jobs of the CI/CD configuration file (see Security/Containers tab)
🏆 Maintainability Score
The maintainability score is calculated based on the following criteria:
- Number of projects using reusable resources, such as templates and R2Devops templates
- Number of projects using up-to-date CI/CD resources (see Job Usage tab)
Inside the Projects Table
The maintainability status displayed on the projects table is based on the composition of the CI/CD configuration file, calculated according to:
- Compliance with templates and template usage
- Presence of hardcoded jobs and the number of lines
🤿 More In-Depth
Weight of Each Criterion
Each criterion has a weight used to calculate the global score, signifying that some criteria are more impactful than others.
Penalty System
To account for critical criteria, a penalty system is implemented. If a criterion is not met, the score is reduced by a certain percentage.
Current criteria with penalties:
- Secrets leaks inside the CI/CD configuration file
- Container image status declared as unsafe, indicating it comes from a non-official registry inside Docker Hub