Kubernetes
This page describes how to run a self-managed instance of R2Devops on Kubernetes.
💻 Requirements
- GitLab instance version >=17.7
- A Redis instance version >= 6
- A PostgreSQL instance version >= 13
- A Kubernetes cluster with:
- One ingress controller(ex: Nginx or Traefik)
- A certificate manager with a ACME provider: cert-manager
- Only if you run external services (PostgreSQL and Redis) in Kubernetes: the ability to provision persistent volumes in your cluster
- Your local environment with CLI to interact with Kubernetes API:
- Write access to the DNS zone of the domain to use with R2Devops
- A user account on the GitLab instance
🛠️ Installation
The Helm chart used in this documentation allows installing all these services
embedded in the chart as dependencies or to use external PostgreSQL
and/or Redis. Both alternatives are detailed below.
📥 Initialize your cluster
- Create the namespace for R2Devops
kubectl create ns r2devops - Add R2Devops repo
helm repo add r2devops https://charts.r2devops.io/
📄 Domain name
You need a domain to run R2Devops. For example, if you have the domain name
mydomain.com:
- R2Devops URL will be
https://r2devops.mydomain.com
-
Create DNS record
- Name:
<r2devops_domain_name> - Type:
A - Content:
<your-cluster-public-ip>
- Name:
🦊 GitLab OIDC
R2Devops uses GitLab as an OAuth2 provider to authenticate users. Let's see how to connect it to your GitLab instance.
-
Choose a group on your GitLab instance to create an application. It can be any group. Open the chosen group in GitLab interface and navigate through
Settings > Applications:
-
Then, create an application with the following information
- Name:
R2Devops self-managed - Redirect URI :
https://<r2devops_domain_name>/api/auth/gitlab/callback - Confidential:
true(let the box checked) - Scopes:
api
- Name:
-
Click on
Save Applicationand you should see the following screen: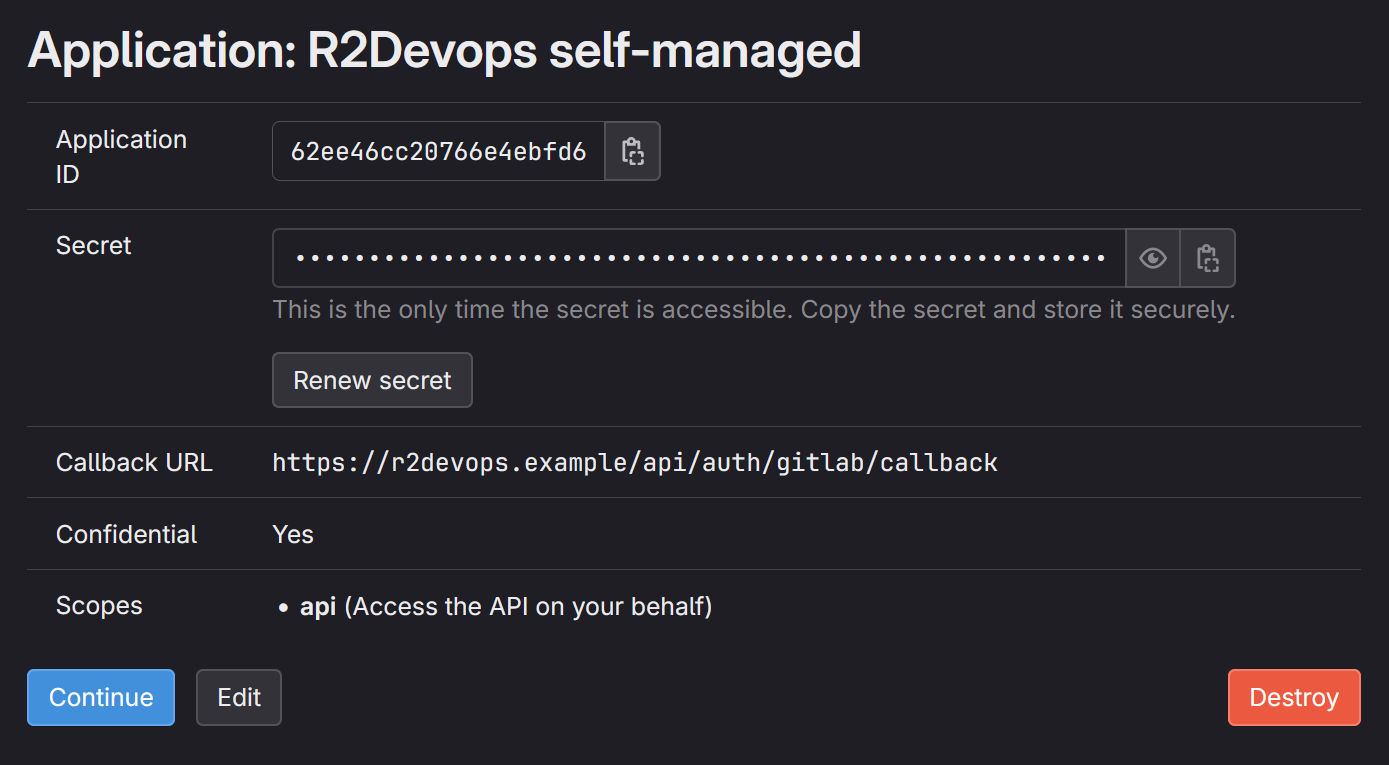
-
Store
Application IDandSecretsomewhere safe, we will need to use them in next step
⚙️ Configure your values
This section describes how to configure your custom values file. The default
values.yaml is available
here.
An example is available at the end of this documentation.
For the following sections, we assume that your custom value file will be
located in your current directory and be named custom_values.yaml
🔐 Secrets
This section is optional. You need to follow this section only if you want to store secrets values as kubernetes secrets instead of writing them in your custom value file.
-
R2Devops secret
Replace all occurrences of
REDACTEDby your R2Devops secrets encoded in base64 and create following secret:secret-key: 256 bit secret key used to encrypt sensitive data (openssl rand -hex 32)gitlab-oauth2-client-id: Application ID of the GitLab applicationgitlab-oauth2-client-secret: Secret of the GitLab application
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: r2devops-secret
namespace: r2devops
type: Opaque
data:
secret-key: REDACTED
gitlab-oauth2-client-id: REDACTED
gitlab-oauth2-client-secret: REDACTED -
PostgreSQL secret
Replace
REDACTEDby your postgres password encoded in base64. If you want to use postgres embedded in this chart, choose the value.apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: postgresql-secret
namespace: r2devops
type: Opaque
data:
password: REDACTED -
Redis secret
Replace
REDACTEDby your redis password encoded in base64. If you want to use redis embedded in this chart, choose the value.apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: redis-secret
namespace: r2devops
type: Opaque
data:
password: REDACTED
🤖 R2Devops
Add R2Devops related configuration in your new values file custom_values.yaml:
-
Add R2Devops domain
front:
host: 'r2devops.mydomain.com'
jobs:
host: 'r2devops.mydomain.com'
# Not using secret for configuration (comment if you use secret)
extraEnv:
- name: SECRET_KEY
value: '<secret-key>'
- name: GITLAB_OAUTH2_CLIENT_ID
value: '<gitlab-oauth2-client-id>'
- name: GITLAB_OAUTH2_CLIENT_SECRET
value: '<gitlab-oauth2-client-secret>'
# Using existing secret for configuration (uncomment if you use secret)
#extraEnv:
# - name: SECRET_KEY
# valueFrom:
# secretKeyRef:
# name: "r2devops-secret"
# key: "secret-key"
# - name: GITLAB_OAUTH2_CLIENT_ID
# valueFrom:
# secretKeyRef:
# name: "r2devops-secret"
# key: "gitlab-oauth2-client-id"
# - name: GITLAB_OAUTH2_CLIENT_SECRET
# valueFrom:
# secretKeyRef:
# name: "r2devops-secret"
# key: "gitlab-oauth2-client-secret"
worker:
replicaCount: 5 # Default is 5. Increase it depending of your needs -
Add your GitLab instance domain and organization
-
If you want to connect R2Devops to a specific GitLab group only: add the path of the group in
organization(to run the onboarding, you must be at least Maintainer in this group)gitlab:
domain: 'https://gitlab.mydomain.com'
organization: '<group-path>' -
If you want to connect R2Devops to the whole GitLab instance: let
organizationempty (to run the onboarding, you must be a GitLab instance Admin)gitlab:
domain: 'https://gitlab.mydomain.com'
organization: ''
-
-
Add your Ingress configuration
ingress:
enabled: true
className: '' # Add class name for your ingress controller
annotations: {} # Add annotation required by your ingress controller or certificate manager -
(Optional) Add your custom Certificate Authority
You can either:
- Reference an existing secret containing your CA public root certificate
using the
existingSecretkey. - Or manually add your CA public root certificate in the values using the
certificateskey.
customCertificateAuthority:
existingSecret: ""
certificates: []
# - name: rootCA.crt # Must have the .crt extension
# value: |
# -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
# (SNIPPED FOR BREVITY)
# -----END CERTIFICATE----- - Reference an existing secret containing your CA public root certificate
using the
📘 PostgreSQL
Add following configuration in your custom_values.yaml file
postgresql:
custom:
host: REPLACE_ME_BY_POSTGRES_HOST
dbName: REPLACE_ME_BY_POSTGRES_DB_NAME
sslmode: 'require'
port: 5432
global:
postgresql:
# Not using secret for auth (comment if you use secret)
auth:
username: REPLACE_ME_BY_POSTGRES_USERNAME
postgresPassword: REPLACE_ME_BY_POSTGRES_PASSWORD
# Using existing secret for auth password (uncomment if you use secret)
#auth:
# username: r2devops
# existingSecret: "postgresql-secret"
# secretKeys:
# adminPasswordKey: "password"
# userPasswordKey: "password"
📕 Redis
Add following configuration in your custom_values.yaml file:
redis:
custom:
port: 6379
host: REPLACE_ME_BY_REDIS_HOST
user: REPLACE_ME_BY_REDIS_USENAME
cert: |
REPLACE_ME_BY_REDIS_TLS_CERTIFICATE
# Not using secret for auth (comment if you use secret)
auth:
password: REPLACE_ME_BY_REDIS_PASSWORD
# Using existing secret for auth (uncomment if you use secret)
#auth:
# existingSecret: "redis-secret"
# existingSecretPasswordKey: "password"
🚀 Install the chart
Run the following command:
helm upgrade -n r2devops --create-namespace --install r2devops r2devops/r2devops -f custom_values.yaml
You have successfully installed R2Devops on your Kubernetes cluster 🎉
Did you encounter a problem during the installation process ? See the troubleshooting section.
📚 Configuration example
This example run in a Kubernetes cluster using:
nginxas ingressControllercert-manager- A clusterIssuer named
letsencrypt-production
front:
host: "r2devops.mydomain.com"
jobs:
host: "r2devops.mydomain.com"
extraEnv:
- name: SECRET_KEY
value: "REDACTED"
- name: GITLAB_OAUTH2_CLIENT_ID
value: "REDACTED"
- name: GITLAB_OAUTH2_CLIENT_SECRET
value: "REDACTED"
gitlab:
domain: "https://gitlab.mydomain.com"
worker:
replicaCount: 5
ingress:
enabled: true
className: "nginx"
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-production"
postgresql:
global:
postgresql:
auth:
username: REDACTED
postgresPassword: REDACTED
custom:
host: "database-1.REDACTED.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com"
port: 5432
dbName: "r2devops"
sslmode: "require"
redis:
auth:
password: REDACTED
custom:
port: 6379
host: "REDACTED"
user: "REDACTED"
cert: |
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
REDACTED
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
⏫ Update
- Update R2Devops Helm repository
helm repo update - Run the helm upgrade
helm upgrade -n $R2DEVOPS_NS --install r2devops r2devops/r2devops -f custom_values.yaml - You have successfully updated R2Devops 🎉